Networking Quiz
Networking Fundamentals Study Guide
Internet
You know what it is :-p
Intranet
An internal, private network that uses the TCP/IP protocol to share resources within a home or organization network.
Extranet
A network connected to the internet that allows limited access to resources from the internet.
VPN
(Virtual Private Network) Allows authenticated users to connect to a network and access resources from a remote location.
Security Zones
The concept of dividing a network into separate zones based on security risks.
Firewalls
A firewall provides a layer of protection to devices on a network by blocking malicious people and code.
Perimeter Networks (DMZ)
A network that connects a intranet to the internet. It's generally placed on a subnet and uses firewalls and other security measures to protect the intranet while providing services like e-mail and internet access.
LAN
(Local Area Network) A network of connected devices limited to a single physical location.
LAN Addressing
All devices on a LAN are assigned an IP address. The IP address is divided into a network ID and a host ID. A subnet mask is used to determine which part of the IP address is the network ID and which is the host ID. The network ID identifies the subnet, and the host ID identifies the host. All devices connected to a network must have the same network ID and a unique host ID. A host ID of binary zero represents the network ID, and cannot be assigned to a host. A host ID of all binary ones represents the subnet broadcast ID, and cannot be assigned to a host. IP addresses can be assigned automatically using a DHCP server.
LAN Reserved Address Ranges
The following IP addresses are reserved for use on private networks:
10.0.0.1 to 10.255.255.254
172.16.01 to 172.31.255.254
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.255.254
VLANs
(Virtual Local Area Network) A VLAN uses a switch to divide the switch's ports into separate broadcast domains.
Leased Lines
A WAN link that is leased by an organization. Different WAN links include T1, T3, E1, E3, DSL, ISDN, P2P wireless bridge and ethernet WAN.
Dial-up
A WAN connection using phone lines. Speeds are slow. Maximum speed is 56 Kbps, but actual speeds are usually lower. Availability is good but reliability is poor, especially in bad weather.
ISDN
A set of communications standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over telephone lines.
T1, T3, E1, E3
WAN links. Speeds are:
T1 - 1.5 Mbps
T3 - 44 Mbps
E1 - 2 Mbps
E3 - 34 Mbps
T1 and T3 are used in America while E1 and E3 are used in Europe.
DSL
(Digital Subscriber Line) A WAN connection phone lines. Data is transmitted digitally. Download speeds are 1 Mbps - 24 Mbps and uploading speeds are 3 Mbps. Availability is good.
Cable
A LAN connection using coaxial cable. The internet signal shares the same cable as the TV signals. Speeds can vary, but are generally fast. Typical download speed is 10 Mbps. Typical upload speed is 6 Mbps. Availability and reliability are generally good.
Wireless Standards
The most important wireless standards and their characteristics are:
| Standard | Speed | Frequency (GHz) | Distance (m) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11a (Wi-Fi 2) | 54 Mbps | 5 GHz | 30 | |
| 802.11b (Wi-Fi 1) | 11 Mbps | 2.4 GHz | 35-45 | Can configure channels to avoid interference |
| 802.11g (Wi-Fi 3) | 54 Mbps | 2.4 GHz | 35-50 | Backward compatible with 802.11b |
| 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) | 300-600 Mbps | 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz | 70 | Backward compatible with 802.11a, b and g |
| 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) | 1.3 Gbps | 5 GHz | 70 | Backward compatible with 802.11a, b and g |
Wireless Security
The most important wireless security methods and their characteristics are:
| Method | Effectiveness | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| WEP | Poor | Only used as a last resort |
| WPA | Poor | Only used as a last resort |
| WPA2 | Good | Very common |
| 802.1x | Very Good | Requires an authentication server |
Point-to-point Wireless
A wireless WAN link. Limited to line of sight connections. Maximum distance is about 25 miles.
Wireless bridging
A method of connecting networks with a wireless connection.
Switches
A network device that connects multiple devices in a subnet. A switch will forward broadcasts to all devices connected to it. transmission speeds are usually 10, 100, and 1000 Mbps. A typical switch will have 4 to 24 access ports. A uplink port is used to connect the switch to another switch or router. Most switches support the creation of VLANs. Ports can be configured to increase security by only allowing specific MAC addresses or disabling unused ports. A switch will separate collision domains. A managed switch can provide the ability to manage and monitor traffic on the network. Unmanaged switched are layer 2 devices, while managed switched are layer 3 devices (see OSI model).
Routers
A router is used to connect networks or subnets. Routers use a routing table to keep track of the networks they connect. All routers must have at least two ports. Routers do not forward broadcasts. In many networks, the router is also the default gateway. Static routes are routes that have been manually configured. Dynamic routes are configured automatically using the RIPv2 and OSPF protocols. A default route is a path that the router uses when another path isn't identified, usually the default gateway. Routers use a "metric" to decide the best way to route data. Routers use the NAT protocol to connect a LAN network with private addressing to a WAN. A computer running Windows Server with "Routing And Remote Access Service" can be configured as a router. Routers are layer 3 devices (see OSI model).
Physical Media
The most important physical media are:
| Media | Speed | Max Length (m) | Susceptibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTP | Cat 5 - 100 Mbps Cat 5e - 1 Gbps Cat 6 - 10 Gbps |
100 100 55 to 100 |
Electrical noise Cross talk Interception |
Very common |
| STP | Same as UTP | Same as UTP | ||
| Fiber | Up to 10 Gbps | Miles | Expensive | |
| Wireless | Up to 300 Mbps | Electrical noise Interception |
||
| Cable (thinnet) | 10 Mbps | 185 | No longer used |
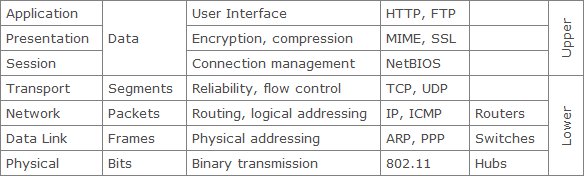
OSI model
An overview of the OSI model:
Protocols
Some common protocols and their ports are:
| Port | Protocol |
|---|---|
| 20, 21 | FTP |
| 23 | Telnet |
| 25 | SMTP |
| 53 | DNS |
| 80 | HTTP |
| 110 | POP3 |
IPv4
IPv4 a 32 bit binary addressing. It does not allow adequate addresses, so methods such as private addressing and NAT are used. IPv4 is being replaced by IPv6.
IPv6
IPv6 is a 128 bit hexadecimal addressing standard.
Names Resolution
Device and domain names can be resolved to IP addresses using DNS and WINS protocols.
Networking Services
An application running at the network application layer and above, that provides data storage, manipulation, presentation, communication or other capability which is often implemented using a client-server or peer-to-peer architecture based on application layer network protocols.
ping
Used to check connectivity with other devices.
tracert
Used to trace the route data takes through a network.
pingpath
Performs a tracert command with pings to determin data loss through the network.
Telnet
A command line interface that allows bidirectional communication with devices on a network.
ipconfig
Lists the computer's network configuration settings.
netstat
Used to check network statistics for the computer.
Protocols
Be familiar with the most common protocols used in networking.
Return to the networking quiz home page.